In today’s fast-paced and highly digital world, cloud computing has become a cornerstone for businesses seeking to improve scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. As companies embrace cloud technology, the process of cloud migration — moving data, applications, and other business elements from on-premise infrastructure to the cloud — has become essential. This transformation is not just a technical shift but a strategic decision that can revolutionize how businesses operate.
However, cloud migration is a complex and often daunting process. It involves careful planning, execution, and ongoing optimization. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of cloud migration, how businesses can seamlessly transition to the cloud, and the various strategies and best practices that can make this shift a success.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud migration offers significant cost savings: Moving to the cloud can drastically reduce infrastructure costs through a pay-as-you-go model.
- Scalability and flexibility are key benefits: Cloud platforms allow businesses to scale their resources up or down depending on demand.
- Choosing the right migration strategy is essential: Different strategies (lift and shift, replatforming, refactoring) serve different business needs.
- Security and compliance should be a priority: Ensuring data protection and regulatory compliance is critical during migration.
- Ongoing optimization is necessary: After migration, continuous monitoring and cost optimization are key to maintaining an efficient cloud environment.
What is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration refers to the process of moving data, applications, and other business resources from on-premise IT infrastructure to cloud-based infrastructure. This can involve a range of different tasks, such as:
- Shifting from physical servers to cloud-based virtual machines.
- Moving applications or databases to cloud environments like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Adopting cloud-native architectures for scalability and flexibility.
Cloud migration offers various benefits, including reduced infrastructure costs, increased agility, and the ability to scale operations quickly. However, to migrate successfully, organizations must thoroughly assess their current infrastructure, choose the right migration strategy, and consider potential challenges.
Why Should Businesses Migrate to the Cloud?
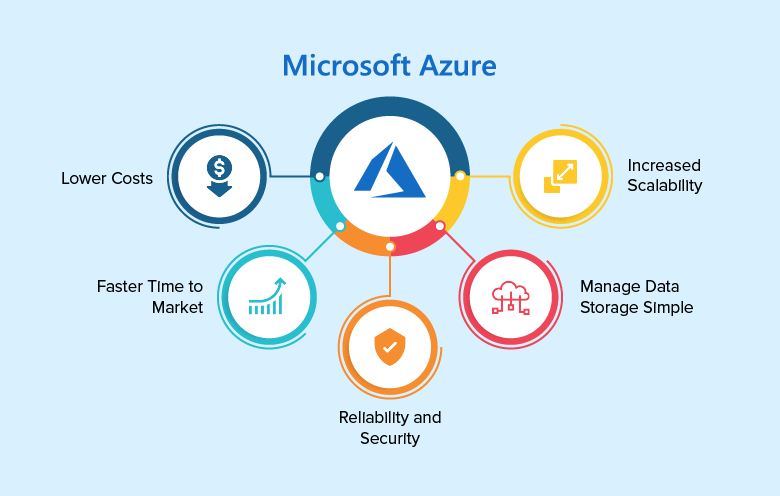
Cloud migration offers several compelling advantages, which is why businesses across all sectors are adopting cloud solutions. Some of the key benefits of moving to the cloud include:
1. Cost Efficiency
Traditional on-premise infrastructure requires significant capital investments in servers, storage, and maintenance. With cloud computing, businesses can adopt a pay-as-you-go model, which means they only pay for the resources they use. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
2. Scalability
One of the biggest advantages of cloud computing is scalability. Cloud platforms offer businesses the ability to scale their resources up or down based on demand. This elasticity ensures that businesses only consume resources as needed, avoiding overprovisioning and reducing waste.
3. Improved Security
Cloud providers invest heavily in advanced security measures to protect data. By migrating to the cloud, businesses can benefit from sophisticated encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates. Cloud services also ensure high availability with backup options and disaster recovery solutions.
4. Increased Flexibility and Collaboration
The cloud allows employees to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility enhances remote work opportunities and fosters better collaboration among teams, especially in a distributed workforce environment.
5. Performance Optimization
Cloud service providers continuously upgrade their infrastructure to meet modern demands. By migrating, businesses can take advantage of cutting-edge technology, including high-performance computing, analytics, and machine learning tools, enabling them to improve operational performance.
The Cloud Migration Process
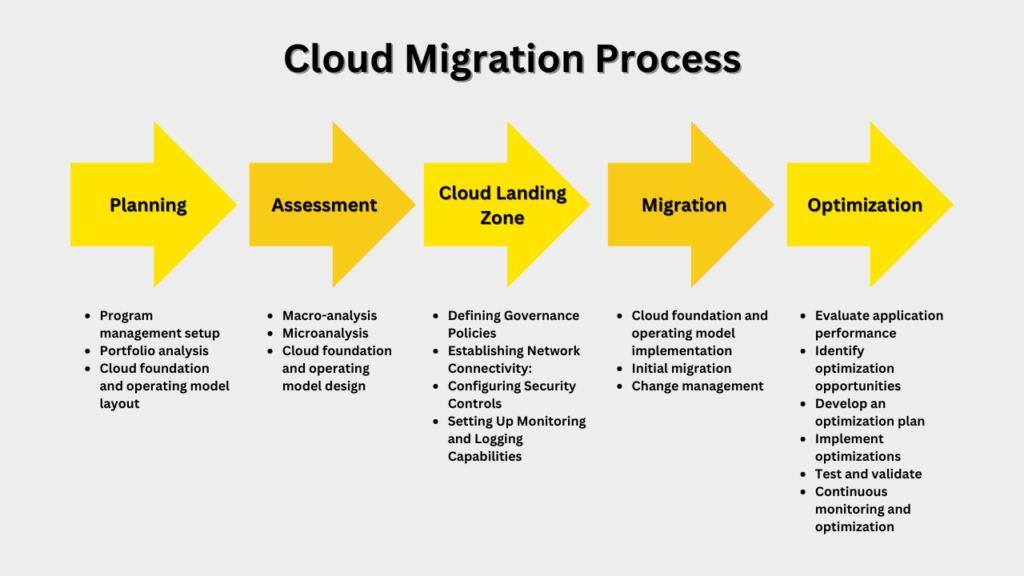
Successfully transitioning to the cloud requires a well-defined process. This process typically includes several key stages:
1. Assessment and Planning
Before initiating cloud migration, businesses must assess their current infrastructure and understand the workloads that will be migrated. This involves identifying the applications, databases, and services that will be moved, and determining the best migration approach.
Key Steps:
- Evaluate existing infrastructure: Understand what resources, data, and applications are in use.
- Identify business needs: Define clear objectives for the migration (e.g., cost savings, scalability, improved collaboration).
- Choose a cloud provider: Research and select a cloud service provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) that aligns with the business needs.
- Develop a timeline: Set a realistic timeline for the migration to avoid disruption.
2. Choosing a Migration Strategy
There are various migration strategies, each suited to different business needs. Choosing the right one is critical for a smooth transition. Common migration strategies include:
- Lift and Shift (Rehosting): Moving applications and data to the cloud with minimal changes. This is often the quickest approach.
- Replatforming: Moving applications to the cloud while optimizing them for better performance.
- Refactoring: Redesigning applications to be cloud-native, leveraging cloud services to their full potential.
- Hybrid Approach: Some organizations may choose to keep certain workloads on-premise while migrating others to the cloud. This hybrid approach is common for businesses with regulatory requirements or legacy systems.
3. Migration Execution
After planning, the migration itself can begin. The execution phase typically involves:
- Data migration: Transferring data to cloud storage.
- Application migration: Moving applications and services to cloud instances.
- Infrastructure provisioning: Setting up virtual machines, networks, and databases in the cloud.
4. Testing and Validation
Once migration is complete, rigorous testing is essential to ensure everything is functioning correctly in the cloud. Testing should cover:
- Application functionality: Verify that applications are working as intended.
- Performance testing: Ensure that the cloud environment meets performance requirements.
- Security checks: Test the security measures to ensure data protection.
5. Optimization and Ongoing Management
After migration, ongoing optimization and monitoring are required to ensure that the cloud environment is running efficiently. This phase involves:
- Cost optimization: Continuously monitor resource usage and optimize for cost savings.
- Monitoring performance: Use cloud tools to monitor performance and address issues proactively.
- Cloud security: Regularly update security protocols and conduct vulnerability assessments.
Challenges of Cloud Migration
While the benefits of cloud migration are significant, there are challenges that organizations may encounter along the way. Being aware of these challenges will allow businesses to plan accordingly and ensure a smoother migration process.
1. Data Privacy and Compliance
Data privacy laws and industry-specific regulations (such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc.) can make cloud migration challenging. Ensuring compliance while migrating sensitive data requires careful planning and a secure cloud environment.
2. Downtime and Business Continuity
Cloud migrations can potentially lead to downtime if not planned and executed carefully. Businesses need to develop a contingency plan to minimize service disruptions during the transition period.
3. Migration Complexity
The complexity of migrating legacy systems or custom-built applications to the cloud can be a challenge. Some applications may need to be refactored or redesigned entirely to work in a cloud environment.
4. Cloud Vendor Lock-in
Choosing a single cloud provider can sometimes lead to vendor lock-in, where businesses find it challenging to switch providers due to the integration and dependencies on specific platforms. Therefore, businesses must weigh the pros and cons of a single cloud provider or a multi-cloud strategy.
Also Read : How Cloud Computing Is Transforming Business Operations And Efficiency
Conclusion
Cloud migration is a strategic move that can unlock numerous benefits, such as cost efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. However, it is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing optimization. By choosing the right strategy, addressing potential challenges, and collaborating with skilled professionals, businesses can successfully transition to the cloud and take full advantage of its capabilities.
As cloud computing continues to evolve, businesses that embrace cloud migration are better positioned to compete in an increasingly digital and dynamic market. Whether you’re a small business looking to scale or a large enterprise aiming for digital transformation, cloud migration is an essential step toward future growth and success.
7 FAQs
1. What is the first step in a cloud migration?
The first step is conducting a thorough assessment of your current IT infrastructure to understand what needs to be migrated, which resources are essential, and what the business goals are.
2. How long does a cloud migration take?
The duration of cloud migration depends on the complexity of the infrastructure, the volume of data, and the migration strategy. Simple migrations may take a few weeks, while more complex migrations could take several months.
3. How do I choose the right cloud provider?
When choosing a cloud provider, consider factors like cost, performance, security, compliance, and the specific features each provider offers. Popular cloud providers include AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
4. Will cloud migration disrupt my business operations?
If executed carefully with proper planning, cloud migration can be done with minimal disruption. However, businesses should expect some downtime, and it’s important to prepare a business continuity plan.
5. Can I migrate to the cloud if I have legacy systems?
Yes, legacy systems can be migrated to the cloud. However, it might require replatforming or refactoring to ensure compatibility with cloud technologies.
6. How do I ensure the security of my data during migration?
Cloud providers offer advanced security protocols, but businesses should also implement additional measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls to protect sensitive data during migration.
7. Is it necessary to use a hybrid cloud strategy?
A hybrid cloud strategy is optional. It is typically used by businesses that need to maintain certain systems on-premises due to compliance or legacy constraints, while migrating other parts of their infrastructure to the cloud.