In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are continually looking for ways to enhance their operations, improve efficiency, and scale at a moment’s notice. Cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer in this regard. By enabling businesses to access and store data, run applications, and host services over the internet, cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations function. It provides unparalleled flexibility, cost-efficiency, and scalability, which are essential for businesses to remain competitive in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud Computing Enhances Scalability: Businesses can scale their operations up or down based on demand, offering unparalleled flexibility.
- Cost Efficiency: With cloud computing, companies only pay for the resources they use, reducing upfront capital expenditures.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud technologies foster better collaboration through real-time sharing of data and applications.
- Enhanced Security and Disaster Recovery: Cloud services provide robust security measures and automatic backup for data protection.
- Industry Transformation: Cloud computing is reshaping sectors like healthcare, retail, and finance by streamlining operations and enabling innovation.
Understanding Cloud Computing in Business
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, over the internet (“the cloud”). Instead of owning and maintaining physical infrastructure, businesses can rent computing resources on-demand from cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
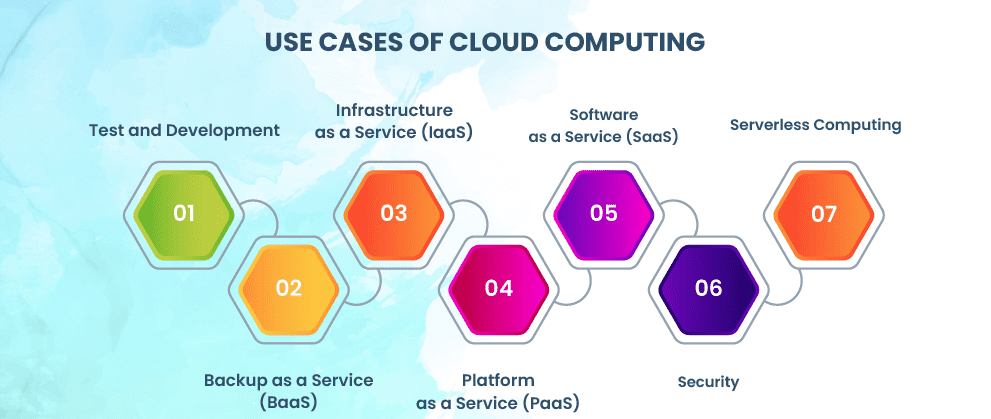
The three main service models of cloud computing are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking. Examples include AWS EC2 and Microsoft Azure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the infrastructure. Examples include Google App Engine and Heroku.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications via the internet, often on a subscription basis. Popular SaaS examples are Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce.
Businesses can choose between public clouds, private clouds, or hybrid cloud solutions, depending on their needs for flexibility, control, and security.
How Cloud Computing Transforms Business Operations
Cloud computing fundamentally alters the way businesses operate, particularly in terms of scalability, collaboration, and cost efficiency. Let’s explore how cloud computing is transforming business operations.
1. Improved Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its scalability. Traditional IT infrastructure often requires heavy upfront investments in hardware and software. Scaling up to meet growing demands or scaling down during slower periods can be time-consuming and costly.
With cloud computing, businesses can scale resources in real-time based on their needs. Whether it’s increasing storage space, adding computing power, or deploying additional applications, businesses can do this instantly with a few clicks.
- Benefits:
- On-demand scaling: Businesses can scale up or down without the need for physical hardware or long setup times.
- Cost-efficiency: Pay only for the resources used, reducing the need for costly infrastructure investments.
- Elasticity: Cloud services automatically adjust to meet fluctuations in demand.
2. Enhanced Collaboration and Remote Work Capabilities
Cloud computing has drastically improved how employees collaborate and work remotely. Cloud-based applications like Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, and Slack have made it easier for teams to share files, communicate in real-time, and work on documents simultaneously, regardless of their physical location.
- Benefits:
- Real-time collaboration: Teams can work on projects in real-time, sharing and editing documents simultaneously.
- Increased productivity: Easy access to shared resources and communication tools reduces downtime and streamlines workflows.
- Remote work: Cloud computing facilitates remote work by enabling employees to access systems, data, and applications from any device, anywhere in the world.
3. Reduced Costs and Better Resource Utilization
The cloud eliminates the need for businesses to invest in costly infrastructure, software, and maintenance. With pay-as-you-go pricing models, companies only pay for the resources they consume, which can be significantly cheaper than maintaining on-premise systems.
- Benefits:
- Reduced capital expenses: Businesses no longer need to purchase and maintain expensive servers, storage, and networking equipment.
- Operational cost savings: Companies can reduce costs associated with software licensing, maintenance, and IT staff.
- Optimized resource allocation: Cloud providers handle infrastructure management, allowing businesses to focus on core activities and innovation.
4. Enhanced Data Security and Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing offers enhanced data security compared to traditional on-site infrastructure. Leading cloud providers implement robust security protocols, including data encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication, to ensure that business data remains protected.
- Benefits:
- Reliable data backup: Cloud solutions typically include automatic backups, which ensure that businesses can recover their data quickly in the event of a system failure or disaster.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud computing simplifies disaster recovery by storing business-critical data offsite, making it easy to restore lost information quickly.
- Advanced security measures: Cloud service providers employ industry-leading security measures to protect business data from cyber threats.
5. Improved Business Continuity and Operational Efficiency
Cloud computing enhances business continuity by enabling smooth transitions in the event of system failures or disasters. Since cloud services are hosted offsite, they are typically more resilient to outages or failures compared to on-premises infrastructure.
- Benefits:
- High availability: Cloud services often offer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) guaranteeing high availability, ensuring businesses experience minimal downtime.
- Efficiency in operations: Cloud-based tools streamline tasks like data management, reporting, and analytics, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently.
- Automatic software updates: Cloud providers manage updates and patches, ensuring that software is always up to date without requiring manual intervention.
Cloud Computing Use Cases Across Industries
Cloud computing has transformed a wide range of industries by enabling faster decision-making, optimizing operations, and providing new ways to serve customers. Let’s look at some of the most significant use cases:
1. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, cloud computing has led to the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and predictive analytics.
- Benefits:
- EHRs and data sharing: Cloud computing enables healthcare providers to store and share patient data securely, improving the coordination of care.
- Telemedicine: Physicians can consult with patients remotely, using cloud-based applications to access patient records and provide treatment plans.
- Predictive analytics: Healthcare providers use cloud-based analytics to predict patient outcomes, personalize treatments, and reduce costs.
2. Retail
Cloud computing has transformed the retail industry by enabling e-commerce, inventory management, and customer personalization.
- Benefits:
- E-commerce platforms: Retailers use cloud-based e-commerce platforms to manage online stores and handle high traffic during peak times.
- Inventory management: Cloud-based inventory systems allow retailers to manage stock levels, track shipments, and forecast demand.
- Customer insights: Retailers leverage cloud-based data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior and personalize shopping experiences.
3. Finance
In the financial sector, cloud computing has improved the efficiency of financial services, including payments, risk management, and customer support.
- Benefits:
- Secure transactions: Cloud computing enables secure payment processing and fraud detection for financial institutions.
- Risk management: Financial companies use cloud computing to run complex risk models and improve decision-making.
- Customer service: Cloud-based customer service platforms, like chatbots and helpdesk software, have improved customer support efficiency.
Challenges of Cloud Computing Adoption
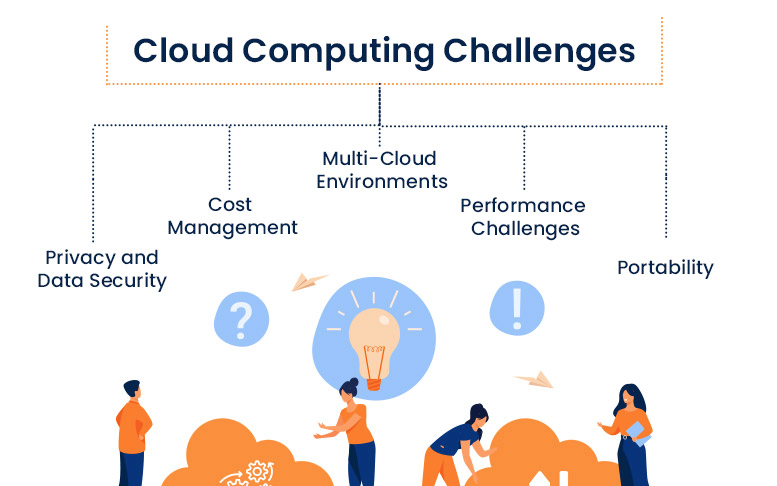
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, businesses may face challenges in its adoption.
1. Data Security and Compliance
Despite enhanced security features, businesses need to ensure their cloud providers comply with industry-specific regulations, such as GDPR in the EU or HIPAA in the U.S. for healthcare data.
2. Downtime and Service Reliability
While cloud providers offer high availability, unexpected downtime or outages can still occur. Businesses need to assess the risks associated with service interruptions and develop contingency plans.
3. Vendor Lock-In
Switching cloud providers can be difficult due to the complexity of migration, leading to potential vendor lock-in. Businesses should ensure they select a flexible cloud provider that allows for smooth transitions if needed.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is fundamentally transforming how businesses operate by enabling scalability, cost savings, improved collaboration, and enhanced security. The ability to access powerful computing resources on-demand gives organizations the flexibility to adapt quickly to market changes, innovate faster, and offer better customer experiences.
While there are challenges in adopting cloud technologies, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. Businesses that successfully integrate cloud computing into their operations will be better equipped to navigate the future of business and thrive in an increasingly digital world.
FAQs
What is cloud computing in business?
Cloud computing in business refers to using internet-based services to store data, run applications, and manage business processes without the need for physical infrastructure.
How does cloud computing improve business efficiency? Cloud computing improves efficiency by providing scalable resources, enabling real-time collaboration, reducing costs, and ensuring high availability.
Is cloud computing secure for business data?
Yes, cloud computing providers implement advanced security measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates to protect business data.
Can small businesses benefit from cloud computing?
Absolutely! Small businesses can reduce capital expenses, access enterprise-level tools, and scale operations quickly with cloud services.
How can cloud computing help remote teams?
Cloud computing facilitates collaboration among remote teams by providing cloud-based file sharing, communication tools, and project management software.
What are the benefits of cloud-based disaster recovery?
Cloud-based disaster recovery offers businesses a fast and reliable way to back up data and restore systems in case of a disaster.
What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid cloud?
Public cloud services are hosted by third-party providers, private cloud is hosted on a company’s own infrastructure, and hybrid cloud is a mix of both.




