In the modern world, digital data is everything—personal information, sensitive business communications, and financial transactions all take place in the virtual realm. As the internet continues to expand and the risks associated with data breaches increase, the need for robust data protection methods has never been greater. Encryption has become the cornerstone of securing data against cyber threats, ensuring privacy, and maintaining trust in the digital ecosystem.
Encryption, once a topic confined to the tech-savvy, is now a necessity for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. This article explores the power of encryption, how it works, and why it is crucial in the digital age.
Key Takeaways:
- Encryption is Essential for Data Protection: It is a fundamental tool for securing sensitive data against unauthorized access.
- Types of Encryption Vary in Use: File encryption, full disk encryption, and end-to-end encryption are some common methods that offer different levels of protection.
- Encryption Enhances Privacy: It ensures that personal information, communications, and transactions remain confidential.
- Compliance with Regulations: Encryption is often required by laws such as GDPR and HIPAA to protect user data.
- Encryption Is Not Flawless: While powerful, encryption systems are only as good as their implementation and management.
What Is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting data from its readable format (plaintext) into a scrambled, unreadable format (ciphertext). Only those with a specific decryption key or algorithm can convert it back into its original, readable form. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be accessed or used by unauthorized parties.
Why Is Encryption Important?
- Protection Against Data Breaches
Data breaches have become more frequent and more damaging. From financial institutions to healthcare providers, no sector is immune to these threats. Encryption ensures that if hackers gain access to a system, the data they steal will be useless without the decryption key. - Privacy Preservation
In an era where personal privacy is continually being eroded, encryption helps to maintain control over sensitive information. Whether it’s your private communications, medical records, or banking details, encryption protects your personal data from prying eyes. - Compliance with Regulations
Laws and regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA mandate the protection of sensitive data. Encryption is often a required method to comply with these privacy regulations, ensuring that organizations avoid hefty fines and reputational damage. - Secure Communication
Encryption secures communication between parties, whether in emails, chat messages, or VoIP calls. It prevents interception of sensitive messages and ensures that private conversations remain confidential. - Maintaining Trust
For businesses, particularly those handling customer information, encryption is a trust-building tool. Customers expect their data to be protected. By implementing strong encryption practices, businesses can build and maintain trust with their clients.
How Does Encryption Work?
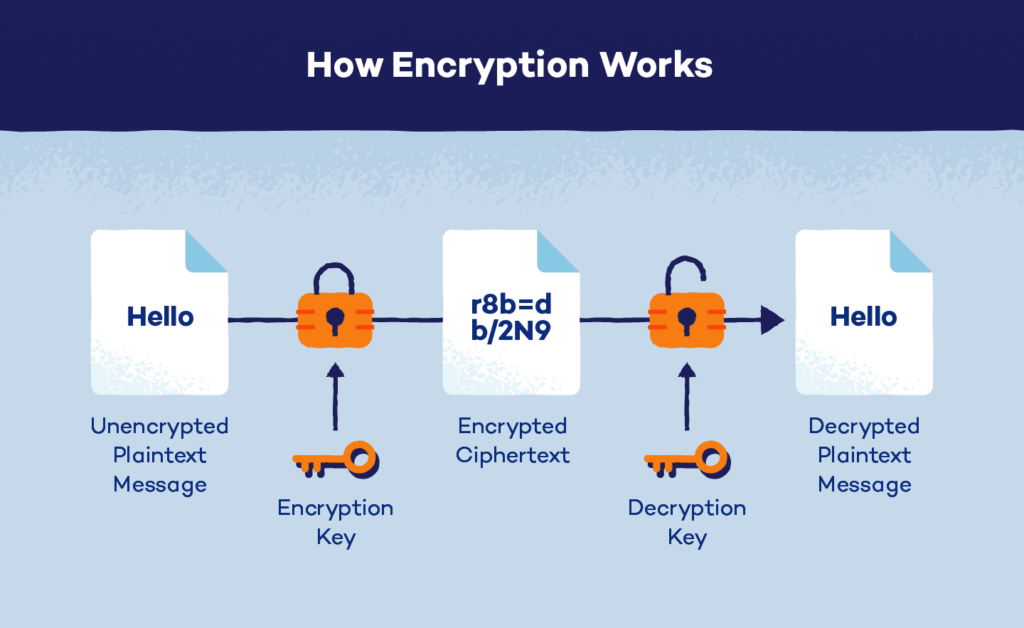
Encryption works by using algorithms to convert data into ciphertext. The complexity of the algorithm and the key used to encrypt the data determines how secure the encryption is. The process involves two main elements:
- The Encryption Algorithm
This is the mathematical procedure that transforms the plaintext into ciphertext. Common encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), RSA, and Triple DES (3DES). - The Encryption Key
The encryption key is a string of bits used by the algorithm to encrypt and decrypt the data. The key’s length determines the strength of the encryption. Longer keys generally provide stronger security.
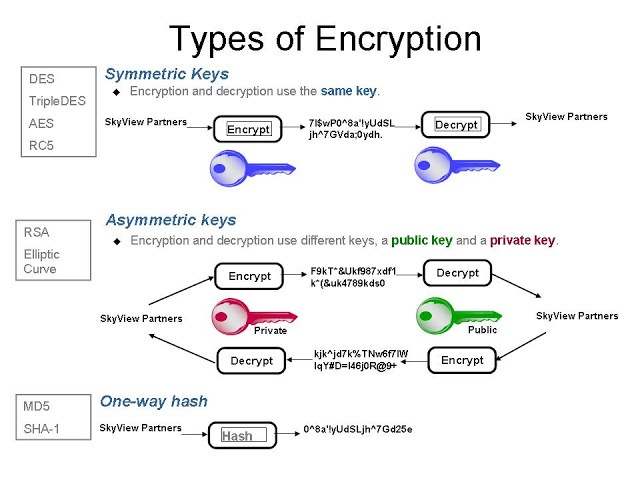
There are two primary types of encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: This method uses a single key to both encrypt and decrypt data. The key must be kept secret to ensure the security of the encrypted data.
- Asymmetric Encryption (Public Key Encryption): This method uses a pair of keys: a public key (which encrypts the data) and a private key (which decrypts it). Only the holder of the private key can decrypt the data.
Types of Encryption
- File Encryption
Encrypting files ensures that sensitive documents are stored securely. Whether on a personal device or in the cloud, file encryption ensures that unauthorized individuals cannot access these files without the decryption key. - Full Disk Encryption
Full disk encryption secures an entire hard drive or storage device. This is particularly important in protecting data on laptops and mobile devices, which are more susceptible to theft or loss. - End-to-End Encryption
Commonly used in messaging applications, end-to-end encryption ensures that only the sender and the recipient can read the messages. Even the service provider cannot decrypt the content, providing maximum privacy. - SSL/TLS Encryption
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are protocols used to encrypt data transmitted over the internet. When you visit a website with “https” in the URL, SSL/TLS encryption ensures that your data, such as login credentials and payment information, is securely transmitted. - VPN Encryption
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) use encryption to secure the connection between a user’s device and the internet. VPNs are widely used to protect privacy while browsing the web, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
Challenges and Limitations of Encryption
While encryption offers robust protection, there are some challenges and limitations:
- Key Management
Proper key management is crucial to encryption’s effectiveness. Losing the encryption key means losing access to the data, and poor key management can lead to unauthorized access. - Performance Impact
Encryption can impact system performance, especially when dealing with large amounts of data. As encryption algorithms become more complex, they require more computational resources. - Legal and Regulatory Concerns
Governments and law enforcement agencies may push for backdoors in encryption systems to combat crime and terrorism. This raises concerns about privacy and the potential misuse of such backdoors. - Human Error
Encryption’s effectiveness relies on proper implementation. Errors in encryption key handling or misconfigured systems can result in vulnerabilities. - Cryptanalysis
Although modern encryption algorithms are highly secure, they can still be vulnerable to cryptanalysis, especially if flawed or outdated methods are used.
Also Read : Cyber Security Jobs For Beginners Start Your Career Today
Conclusion
Encryption stands as the guardian of data in the digital world, ensuring privacy, security, and trust. Whether for personal communication or enterprise-level security, encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding our digital lives. As technology continues to evolve and cyber threats grow in sophistication, encryption will remain one of the most effective means of defending against unauthorized access and data breaches. Understanding how encryption works, its importance, and its limitations is key to ensuring we can continue to protect our data in an increasingly connected world.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of encryption?
Encryption’s primary purpose is to protect data from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality and privacy for sensitive information.
2. How do I know if my data is encrypted?
Look for indicators like HTTPS (for web traffic) or locked icons in communication apps. You can also use encryption software to check the status of your files.
3. Can encryption be hacked?
While encryption is highly secure, no system is entirely immune to hacking. However, the strength of modern encryption makes it exceedingly difficult to break.
4. Is encryption necessary for all businesses?
Yes, especially for businesses handling sensitive customer data. Encryption helps comply with regulations and builds trust with clients.
5. What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys—public and private.
6. How can I encrypt my emails?
You can use email encryption services like PGP or S/MIME, or opt for encrypted email providers like ProtonMail.
7. Can encryption slow down my device?
Yes, encryption can have a minor impact on device performance, especially when encrypting large volumes of data or using complex algorithms.




